Dermatitis Herpetiformis, Signs Of Celiac Disease On The Skin? – Being Parents
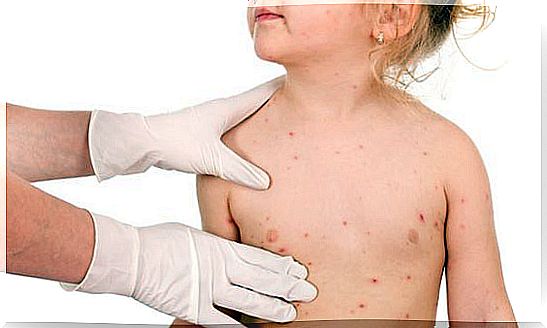
Dermatitis herpetiformis is an inflammatory and autoimmune skin condition. This pathology is characterized by the presence of itchy, chronic and recurrent skin lesions. This disease is considered to be a precursor to gluten intolerance.
Many gastroenterologists consider this rash to be a sign of celiac disease. In this Parenting article, we give you more details about dermatitis herpetiformis , also known as Duhring’s disease.
Dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten sensitivity
Duhring’s disease is considered to be an epidermal manifestation of a certain intolerance or sensitivity to gluten. It is for this reason that it affects people with celiac disease.
The fact that these rashes occur in 5% of the population with celiac disease is not trivial. For specialists, there is a close relationship between the two conditions because they share the same genetic basis.
Symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis

According to data collected by various celiac associations around the world, 90% of people with this skin pathology do not present digestive symptoms after ingestion of gluten. Because the only manifestation of this intolerance is linked to skin rashes.
Usually, patients with this type of dermatitis experience their first symptoms around the age of 20. However, there have already been cases of children suffering from these symptoms at a very young age.
Another fact that the researchers brought up is that this type of disease mainly affects men. For reasons still unknown, this manifestation is uncommon in women, although a few cases have been identified.
Appearance, diagnosis and treatment
The appearance
Among the patients consulted, the vast majority mentioned an extremely uncomfortable skin disease. It is no accident that dermatitis herpetiformis can cause friction injuries and even severe itching.
This is because Duhring’s disease manifests itself mainly in the folds of the skin. The elbows and knees are thus the parts of the body most affected. One or more rashes of various appearances are present, in a spaced or concentrated fashion.
This is manifested by red spots and dryness of the skin. It may even have blisters and severe itching.
The diagnosis
Thus, the diagnosis of this condition necessarily involves a skin biopsy, which consists of taking samples of the healthy epidermis in order to analyze the presence of anti-transglutaminase antibodies.
Once it has been reliably determined that the patient has this condition, simple treatment is indicated.
The treatment
It is about leading a gluten-free diet. Therefore, the person will eliminate from his diet all products containing wheat, oats, barley and rye.
By following this strict diet, the blisters and rashes should subside and go away. The doctor may also suggest some creams, topical treatment or medication to speed up wound healing.
Can dermatitis herpetiformis cause complications?

As it is an autoimmune pathology, like celiac disease, this condition also causes significant complications. It is necessary to take them into consideration because these sequelae are not visible to the naked eye and go beyond serious and severe skin damage.
This poor intestinal absorption of nutrients from food caused by gluten can cause other health problems. We are talking about much more serious concerns that involve high risks for the patient.
Cancers and digestive lymphomas are proof of this. This is why it is imperative to be able to diagnose the disease as early as possible, but also to have an adequate gluten-free diet. Skin lesions may be almost imperceptible or have no digestive effect.
However, the after-effects can be harmful and even lead to the death of the poorly treated celiac person. It is no coincidence that celiac disease is known as silent disease.