Dental Expulsion In Children – Being Parents
Children’s joy in their games and sports can sometimes be clouded by blows and trauma in the mouth. During these accidents, it is possible for dental expulsion to occur in children.
This means that a tooth is ejected from its location. It is a time of tension, pain and stress. As a parent, you need to know what to do to calm and help your child at this time. Here are a few tips.
What is dental expulsion in children?
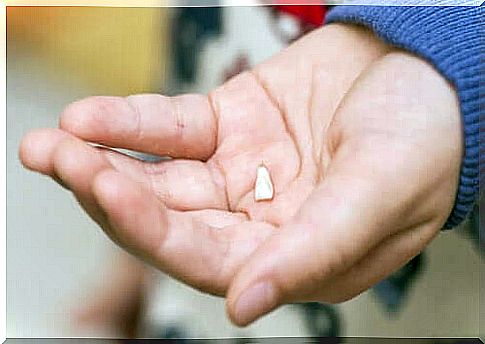
Dental expulsion in children is a tooth that is completely pulled out of the socket where it was implanted. The tooth is expelled from the mouth in its entirety (crown and root of the tooth) without its structure being compromised.
Detachment of a tooth from its natural place occurs as a result of trauma or shock. This is considered to be an urgent dental trauma. For this, it is therefore necessary to act quickly to resolve the situation.
Dental expulsion in children can occur in both primary and permanent dentition. This phenomenon particularly affects the upper incisors. In fact, due to their location, they are more exposed to a shock received in the mouth.

What to do with dental expulsion in children?
When undergoing this type of trauma, the child suffers, bleeds and a stressful situation is generated. The adult responsible for the child must remain calm in order to act quickly and appropriately. The steps to follow will be different if the tooth expelled from the mouth is a baby tooth or a permanent tooth.
The expulsion of a temporary tooth
In cases where the expelled tooth is a baby tooth, it should especially not be reimplanted in the socket. This is because it can damage the germ of the permanent tooth that forms inside the bone.
The best thing to do is to go to the dentist urgently. The dentist will carefully examine the entire damaged area. He will also do x-rays to check for any bone fractures and make sure there are no tooth fragments left in other areas.
The expulsion of a permanent tooth
In cases where the tooth expelled from the mouth is permanent, the procedure to follow is different. First of all, it must be ensured that the child does not present serious complications requiring urgent hospitalization (loss of consciousness, bleeding, vomiting, confusion). Then the adult should contact a dentist for help and advice. The steps to follow are as follows:
- Find the tooth : try to find the extruded tooth as quickly as possible. Take it by the crown and never by the root. It is essential to keep the root intact.
- Clean the tooth : if the tooth found is very dirty, it should be washed with clean water for ten seconds. It is essential to grab it by the crown. Indeed, do not touch, rub or dry the area roots.
- Reposition the tooth : try to place the tooth in the correct position in the hole it left in the mouth. And this, before a clot forms in the socket. Have your child bite into a gauze or tissue to hold the tooth in place. We must call the emergency dentist.
- Tooth transfer : if the tooth cannot be put back in its socket, it is necessary to keep it moist. It can also be transported in a glass of milk or physiological solution. Or, allow it to be transported in the child’s mouth, under the tongue, avoiding of course swallowing it. Do not place it in a handkerchief or a towel so that it does not become dehydrated.
- Consult the dentist urgently : bring the child to the dentist as soon as possible, preferably within an hour of the trauma. The faster the situation is resolved, the better the prognosis.
The treatment
When the child arrives at the clinic, the dentist will be the person responsible for the situation. Child care will therefore be the priority. The accompanying adults must control their anxiety to allow the dentist to act and reassure the child.
The dentist will perform a clinical and radiographic examination. If the affected tooth is permanent, it will be replaced in the socket (or its position will be checked if the patient has already re-implanted it).

Then another check-up x-ray will be taken with the tooth in place. The child should try to bite gently on a test performed by the dentist to test for the bite. This will therefore ensure that there is no interference with the occlusion.
To maintain the re-implanted tooth, the dentist will make a splint to immobilize it. This involves joining the reimplanted tooth with orthodontic wire and composite (aesthetic material used in fillings) to neighboring teeth to prevent any type of movement. Then the splint stays in place for at least three weeks.
The use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs will be necessary to avoid infections, reduce pain but also promote healing. Injection of the tetanus vaccine will also be necessary.
In case of expulsion of a temporary tooth, it is also necessary to go quickly to the dentist. The dentist will monitor the level of hard and soft tissue damage.
Depending on the age of the child and the time remaining for the dental replacement, the fitting of a prosthetic appliance may be necessary. This has the function of maintaining space for the permanent teeth. But also to restore the aesthetic appearance and functionality lost.
Recommendations after dental reimplantation
Once the dentist has re-implanted the tooth in its socket and immobilized it, he will indicate certain special treatments:
- Dieting with soft-textured foods: Avoid foods that require a lot of chewing. Favor light and cold foods such as smoothies, yogurt and ice cream. They will help in better recovery.
- Give the affected area time to rest : chew and bite on the other side. Above all, do not bite with the reimplanted tooth.
- Maintain good oral hygiene : do not suspend your oral hygiene. It is essential to carry out carefully and delicately brushing in the damaged area. Preferably use a soft toothbrush. The dentist may also indicate supplementation with an antiseptic rinse.
- Perform periodic dental check-ups : the dentist will schedule periodic visits to check the progress and check the condition of the splint. Once the immobilization has been removed, the checks will be carried out one month, 3 months, 6 months and one year after the first visit. The re-implanted dental element may require root canal treatment at some point.
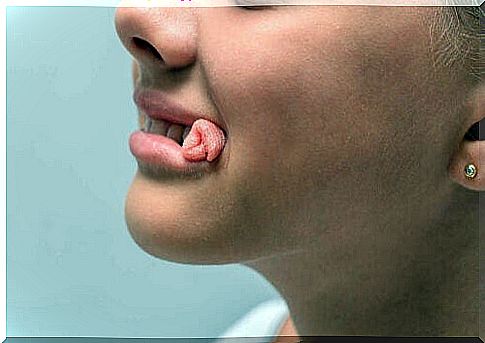
- Be aware of the risk of complications : the dentist will give warning signs to special attention. Here are some examples of complications such as the appearance of fistulas, discharge of pus, severe pain but also swelling of the face.
How to prevent dental expulsion in children?
To avoid dental expulsions in children, it is important to avoid situations that promote bumps and falls. Among other things, they must avoid jumping from moving swings and running around the edges of swimming pools.
When the upper teeth grow outward, they present a greater risk of injury. In this case, the treatment of these malpositions by orthodontics then becomes a real means of prevention. In addition, in the case of young children, it is advisable to avoid using baby walkers.
It is also recommended to use mouth protection when practicing risky sports and when cycling or rollerblading. The mouthguard is a transparent device that is placed in the mouth. It is an excellent ally in preventing tooth expulsion. Indeed, it helps to cushion the blows on the jaw and to protect the dental elements.
Acting quickly is the key
In the end, when faced with a dental expulsion in a child, knowing what to do and acting quickly, with determination and calmly will make the difference. The sooner you go to the dentist, the better the prognosis for the lost tooth.
Pits to the mouth can be avoided, but sometimes they are unavoidable. If your child loses a tooth as a result of trauma, you already know what to do to help him or her.