Melanoma In Children And Adolescents – You Are Parents
Melanoma in children and adolescents is not one of the most common pathologies. However, you must take the necessary precautions to prevent it or to protect your children’s skin.
Also, children who suffered more than three severe burns during childhood have a higher risk of developing melanoma in the future.
What is melanoma?
Melanoma in children and adolescents is rare. Indeed, it only accounts for 1.3% of all cancers in patients under 20, according to studies published in the European Journal of Cancer.
Melanoma is the most aggressive skin cancer if it spreads throughout the body. Therefore, it is very important to detect it early. And thus to ensure its subsequent excision, treatment and follow-up.
Indeed, this tumor is more common in adults. However, it also appears in adolescents with too many moles and a history of melanoma.
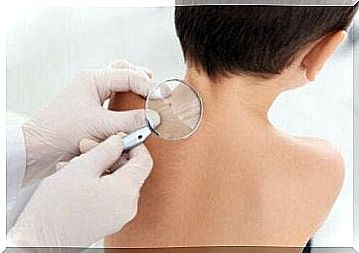
Differences between melanoma and mole
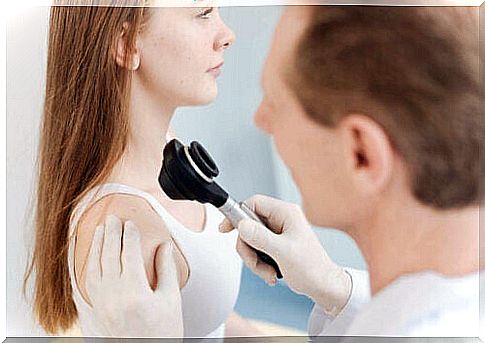
It is important to check moles once a year. This control is usually done by the dermatologist during the consultation by means of a clinical physical examination or with the dermatoscope. What characterizes a malignant lesion is whether it is a new spot or an existing spot that has changed properties.
In addition, the American Cancer Society explains the ABCDE rule to us. This rule makes it possible to carry out an injury control yourself at home. We must therefore check these different points called ABCDE:
- A for asymmetry : there is no similarity between the two halves of the mole.
- B like edges : the edges are ill-defined or irregular.
- C for color : the color is not uniform. We can even observe different nuances.
- D in diameter : the mole has increased in size compared to the previous control.
- E for evolution : shape, size or color changes over time.
In addition, there is another method of analyzing moles. This is the “ugly duckling sign”. In other words, a mole is suspected that differs in some characteristics from other moles present on the child’s body.
Risk factors for melanoma in children and adolescents
There are risk factors that can be changed and others that cannot. Also, just because a person has one or more of the predisposing factors does not mean that they will develop melanoma in the future. Here are some of those factors:
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays
- Having a lot of moles.
- Dysplastic nevi (atypical moles).
- Dysplastic nevus syndrome
- A family history of melanoma
- But also a history of skin cancer
- Xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Finally, having fair skin, light eyes, and blonde hair.
What can be done to prevent melanoma in children and adolescents?
The vast majority of melanomas in children and adolescents cannot be prevented. Indeed, prevention is difficult because they develop from a DNA mutation. However, steps and precautions can be taken to protect the skin and try to prevent melanoma.
Specialists particularly recommend avoiding sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. These are the hours when the sun and its rays are the most aggressive. Even if you apply sunscreen on children, exposure is not beneficial to the skin.
Sun protection in all its forms
Babies under 6 months should not be exposed to ultraviolet rays, even when applying a sun protection factor. Anyone exposed to the sun’s rays should apply a broad spectrum (UVA / UVB) sunscreen greater than or equal to 50. In addition, the sunscreen should be reapplied every 2 hours to exposed areas of the body.
Intermittent sun exposure, such as during vacations, or severe sunburns in childhood carry a high risk of melanoma.
The use of tanning salons, tanning booths or artificial sunscreens is not recommended because of the damage they cause to the skin. The UV rays emitted by tanning beds can cause cell mutations and even death. They also decrease the skin’s own immunity.

Do regular skin checks
One of the least frequent medical check-ups for people is the annual mole checkup with the skin specialist. In fact, a monthly skin self-check should be done routinely at home.
Those with a history of melanoma, who have atypical moles, or have a family member with this type of skin cancer should be subject to more stringent checks.
Thus, during medical examinations, the dermatologist can choose to take photos to observe the evolution of the lesions over time.
Prevention of melanoma in children and adolescents as a treatment
Childhood is a time in life when children need to be very careful about sun damage. In addition, the burns that are generated here will determine the manifestations of the skin in the future.
Finally, it is very important to sensitize and educate children on the importance of using the sun protection factor. In addition, you can resort to UV protective clothing that ranges from t-shirts to hats and even sunglasses.