Thrombosis And Pregnancy: A Dangerous Duo – Being Parents

Thrombosis and pregnancy form a dangerous duo. However, with early diagnosis and the adoption of certain measures, the situation can be overcome.
Remember that blood circulation can be affected by the presence of a clot. This results in what is called thrombosis. Knowing more about its characteristics will help prevent this disease.
During pregnancy, the chances of suffering from thrombosis increase. This is due to the fact that the blood of the pregnant woman is more likely to form clots due to some changes in coagulation or in the placenta.
In addition, the uterus grows and thus decreases blood circulation, especially in the lower limbs. Find out why thrombosis and pregnancy cannot be combined.
What is thrombosis?
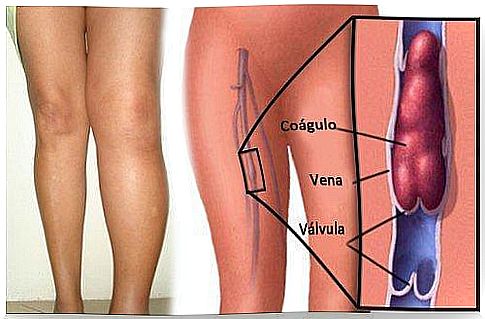
We call “thrombosis” a clot that forms inside the blood vessels, especially at the extremities. However, this is one of the possible complications that can occur during pregnancy.
Thrombosis is a very common pathology in women who have varicose veins, are sedentary, obese or are over 30 years old. The risk of suffering from it increases as the pregnancy progresses.
Thrombosis can appear on the surface or in the veins. It can cause serious complications. This is because clots can break off, blocking blood flow and causing pulmonary embolism. It is estimated that pregnancy increases the risk of suffering from this disease by 10%.
Symptoms of a combination of thrombosis and pregnancy
Fluid retention in body cells is very common during pregnancy, especially in the legs. This inflammation may however be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Fever.
- Cough and chest pain.
- Heat and swelling of the calf (phlebitis).
- Tachycardia and difficulty in breathing.
- Redness at the affected extremity.
- Sharp pain that extends from the thigh to the calf.
Possible causes of thrombosis during pregnancy
Although pregnancy is a risk factor, it can also combine with the following causes:
- Obesity.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
- Intestinal disorders.
- Cesarean or premature delivery.
- Coagulation disorders.
- Pressure exerted by the growing fetus.
You can reduce your risk of developing thrombosis during pregnancy if you help lessen the effects of the previous causes.
Complications of pregnancy in thrombosis
Suffering from thrombosis during pregnancy can lead to the following consequences:
- Restriction of fetal growth.
- Miscarriages until the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Placental abruption. This is the partial or total separation of the placenta from the uterine wall. In addition, this complication is accompanied by severe hemorrhage, endangering the life of both mother and baby.
Thrombosis treatments
Treatment will depend on the type of thrombosis you have. Here are the two types of thrombosis that exist:
- Superficial thrombosis. In this case, the treatment will be based on prophylactic measures such as elevation of the legs, physical exercise, the use of compression stockings or special elastic socks. This treatment is sometimes supplemented by taking an anti-coagulant such as aspirin.
- Deep thrombosis. For this type of thrombosis, the treatment contains heparin-type anti-coagulant drugs.
How to prevent thrombosis during pregnancy?
In itself, the best way to avoid this pathology is to increase physical exercise, which promotes blood circulation. The following methods can also be applied in addition:
- Avoid working under high temperatures.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients.
- Avoid sitting or lying down for a long time.
- Go for walks frequently, with a minimum of 150 minutes per week.
- Do not wear tight-fitting clothing that impedes good blood circulation.
- Do not cross your legs for too long. This prevents venous return.
- Consume medications prescribed by the doctor to prevent or treat thrombosis during pregnancy.
- If you are at rest, ask your doctor for advice on rotating and raising the legs.
- Have a specific medical follow-up which includes coagulation examinations, Doppler ultrasounds, blood pressure checks and exploration of the veins.
- Another good alternative is to carefully monitor your diet. Avoid food too high in salt.
In short, thrombosis and pregnancy form a dangerous duo. However, with early diagnosis and proper medical management, you can overcome the situation.
In addition, it is essential to carefully observe the symptoms and drink enough water. This will greatly reduce the chances of suffering from thrombosis.